A representative from our team will reach out to you soon.
DPA
DPA (Discrete Processes Automation) is a real-time analytical platform for monitoring CNC machines. It offers an objective assessment of equipment status and allows seamless integration with a majority of existing CNC equipment in the market, eliminating the need for modifications or prolonged, expensive setup
BASIC COMPONENTS OF DPA
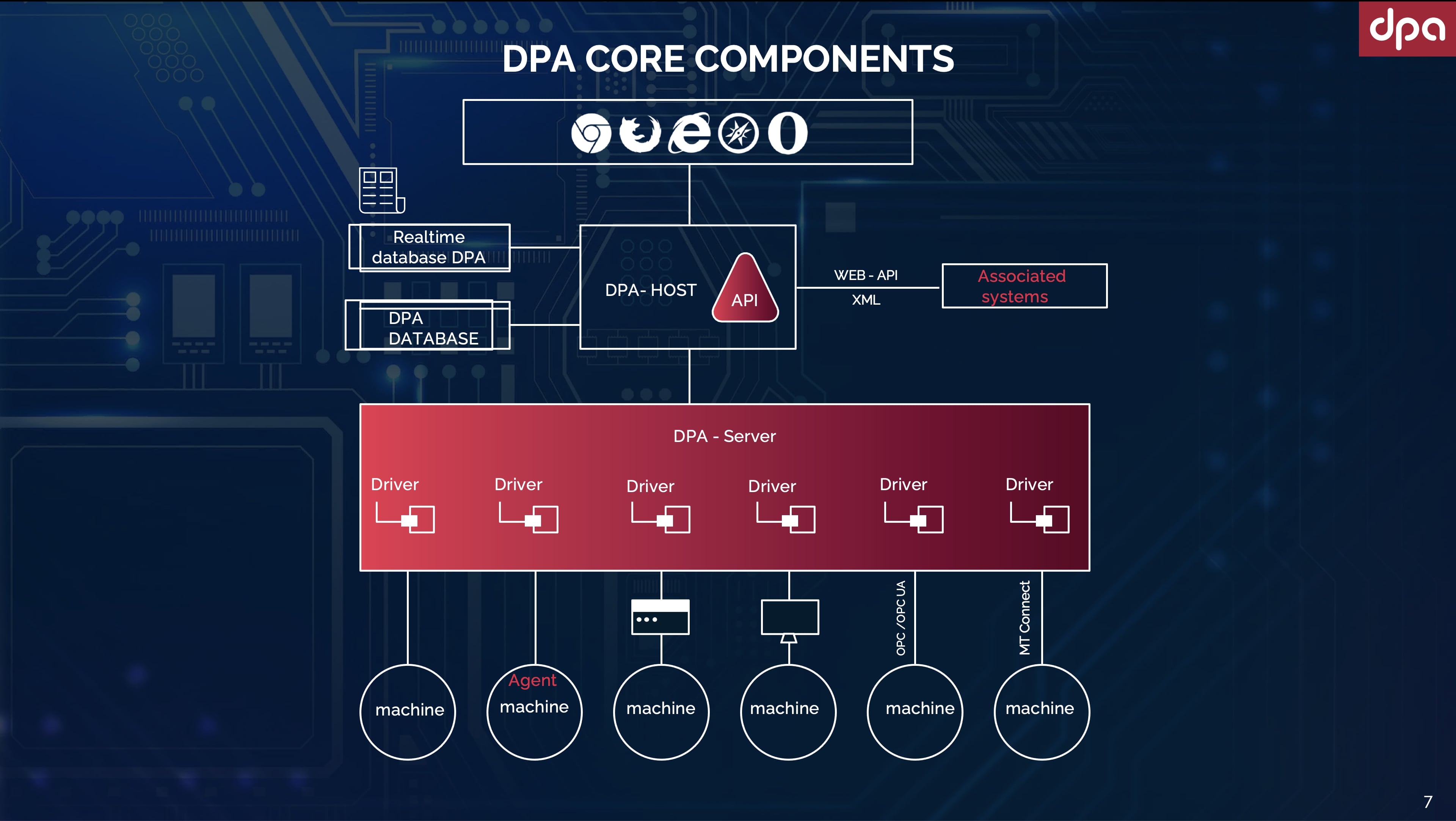
DPA Server – is responsible for direct interaction with the monitoring equipment. It collects data, carries out their primary processing and transmits them to the Host.
DPA Host – aggregates and processes data from DPA servers, writes them to the DPA database and DPA indicator files. It is also responsible for the operation of the user interface.
DB DPA – is a relational database designed to efficiently store system tables, reference information, meaningful machine and user data.
DB Realtime DPA - is a real-time database designed to optimize writing and reading of frequently changing machine data and to streamline the use of the server resources.
A driver contains the functionality to control and access the data of the CNC control panel and does not require any additional hardware device. It allows the interaction of the system components with a certain type of device.
A virtual Driver - is a driver that emulates the operation of a machine tool.
An Agent - is an intermediary software component that provides logging and transmission to the server of the data connected with the equipment operation and state. The agent is installed directly on the machine (not on all types of machines, this information should be clarified in X-tensive).
Basic Functions
-
analysis and visualization (graphical representation), collected directly from the equipment, machine data (obtaining information from controllers and digital sensors);
-
real-time data management (alarms and events) requiring a response or manual input of values;
-
setting time standards for operations and resource requirements, as well as the formation of missing norms and technologies for production history;
-
Job by technology (sequence of operations with identification of standard time and resources): facilitates reading and comparison of the loaded and executed NC code;
-
Control of deviations and immediate reaction to such faults minimize scrap production and losses and ensure realistic manufacturing scheduling;
-
The integration of M&R and Quality Control Departments takes into account maintenance and quality control operations and allows optimizing shift work schedules to maximize the machine tool productivity in the context of the existing manufacturing facilities, so that orders are fulfilled on time;
-
Choice of criteria and methods for plan optimization, data exchange with other information systems (external APS and BI systems);
-
Ability to maintain reference information database;
-
Access control management permitting access to the system's resources, accounts and sessions of the users, including the access to the Employee Shift Scheduling Database;
-
Creating report forms




